October 24, 2025
Implementing Zero-Trust Architecture: Strengthening Network Security with Continuous Authentication
Implementing Zero-Trust Architecture: Strengthening Network Security with Continuous Authentication
Ever wondered what would happen if a hacker got into your network? What if a criminal could switch devices anonymously? Scary, right? Traditional security solutions fail in the digital age. Here comes, ZTA: Zero-Trust Architecture. This game-changer assures no one, not even insiders, is trusted by default. This blog post will discuss about how Zero-Trust and ongoing authentication can protect you in a world where cybersecurity is always changing phases.
What is Zero-Trust Architecture?
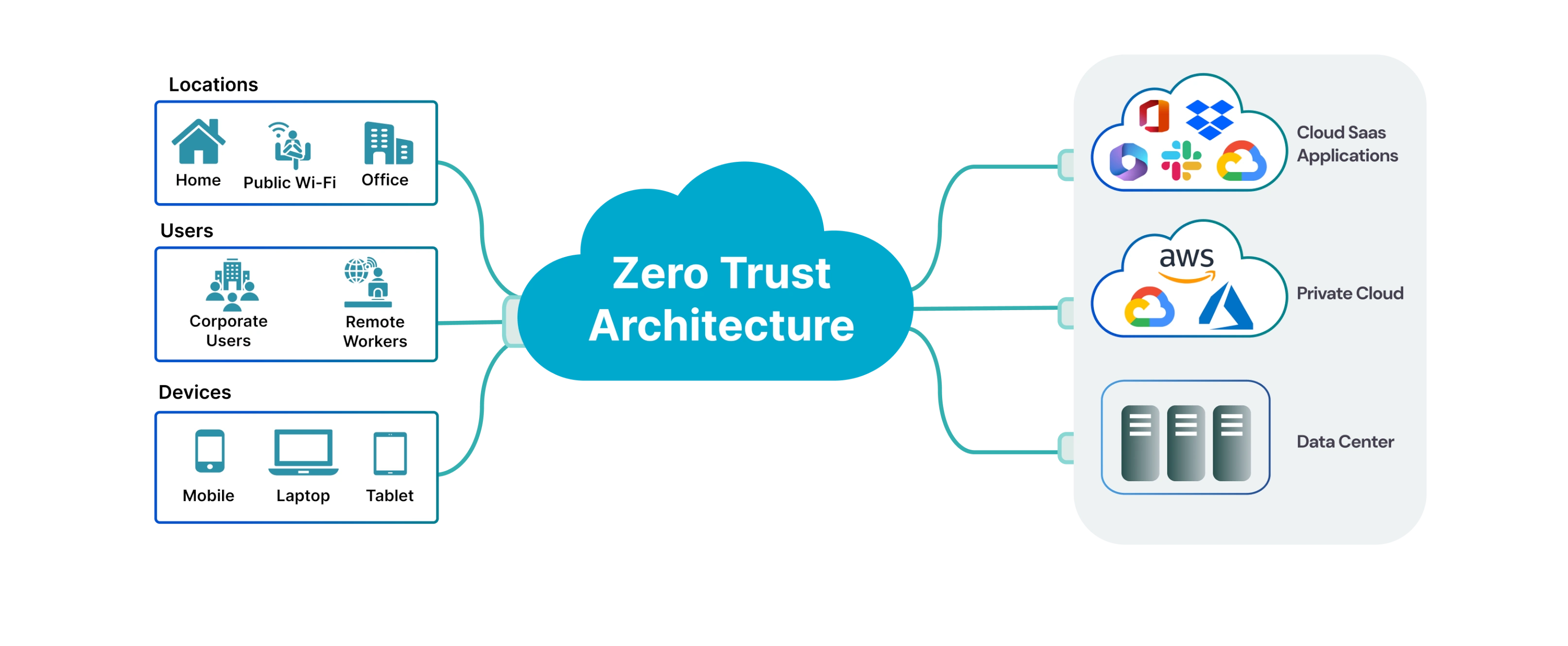
What's Zero-Trust Architecture? Imagine a security mechanism that distrusts everyone within and outside the network. Sounds intense? However, Zero-Trust follows the philosophy of Never trust, always verify.
Unlike typical systems that trust users once within the network, Zero-Trust is always vigilant. Every request, internal or external, is thoroughly checked before access is given. Continuous validation reduces risks and stops cybercriminals.
Like a club bouncer, it checks IDs, names, and doesn't let anybody in without a permit. This ongoing procedure keeps everyone in check.
Why Zero-Trust is Necessary in Today's World?
Why do I need Zero-Trust? In simple terms, cyber attacks are becoming more sophisticated daily. Trusting someone in your network is no longer adequate due to AI-driven assaults, insider threats, and weak passwords. Hackers using stolen credentials to get into your system cause pandemonium.
In a world of remote workers and cloud-based technologies, zero-trust is our defence against such dangers. Zero-confidence guarantees that confidence is earned at every stage in today's world of verification.
How Zero-Trust Architecture Works?
How does it operate in practice? It relies on identity management, device trust, and network segmentation.
Users are regularly validated when they log in to your system. This guarantees that an attacker who obtains access to a user's device can't access vital systems without extra checks. Additionally, devices are constantly checked for compromise.
Now for the details: Continuous authentication may be achieved using JWT tokens. Let's see an example in Python:
import jwt
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
def generate_token(user_id):
payload = {
'user_id': user_id,
'exp': datetime.utcnow() + timedelta(hours=1),
}
return jwt.encode(payload, 'secret_key', algorithm='HS256')
def verify_token(token):
try:
payload = jwt.decode(token, 'secret_key', algorithms=['HS256'])
return payload
except jwt.ExpiredSignatureError:
print("Token expired!")
return None
except jwt.InvalidTokenError:
print("Invalid token!")
return None
token = generate_token("user123")
print(verify_token(token)) This code generates a JWT token and verifies its authenticity with each request. No token? Access denied. Simple.
Zero-Trust Architecture Challenges
Zero-Trust seems like the right solution, but it's not always easy. Legacy system integration is difficult. Many older infrastructures assume trust is implicit once in the network. Implementing Zero-Trust can be a major undertaking.
Zero-Trust requires ongoing monitoring, therefore you'll need the necessary tools and staff to provide continuous verification without bottlenecks or performance issues. Keeping an eye on every part of a vast stadium is difficult but vital.
Key Technologies Enabling Zero-Trust
Without cool tech, Zero-Trust is impossible. AI and machine learning help your security system recognize suspect behavior, such as unusual user patterns.
IAM systems, which restrict access to authorized users and devices, are also important. MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) adds an extra degree of security by requiring an attacker to use another form of authentication if a password is compromised.
Here's a quick example of AI-driven anomaly detection with Python:
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
import numpy as np
# Example user activity data
user_data = np.array([[1, 100], [2, 101], [3, 200], [4, 500]])
model = IsolationForest(contamination=0.2)
model.fit(user_data)
outliers = model.predict(user_data)
print(outliers) # -1 for anomaly, 1 for normal activityThis helps your system detect strange patterns and block access before damage.
Best Practices for Implementing Zero-Trust
How do I integrate this in my organization? Some best practices:
- Start small: Secure your most important assets and expand from there.
- Employ least privilege: Limit user access to necessary resources.
- Continuously monitor: Keep an eye on user behavior, device status, and network activities.
- Integrate IAM solutions: Strong Identity and Access Management systems with multi-factor authentication.
Adopting these ideas gradually will build a Zero-Trust atmosphere that grows stronger.
Conclusion
ZTA is the future of cybersecurity, not a trend. Continuous authentication makes it tougher for attackers to enter by always checking system access. Zero-Trust is the method to improve your security.
830 views
