October 07, 2025
Storing Passwords Securely: A Guide to Hashing and Salting in 2025
Storing Passwords Securely: A Guide to Hashing and Salting in 2025
What if your complete user database leaked tomorrow? Think about it. Keeping plaintext passwords is game over. An attacker may quickly enter into your users' accounts, reuse their passwords on other sites, and cause chaos.
Unfortunately, this nightmare is still widespread in 2025, but it is avoidable. What is the secret? Traditional hashing and salting. These easy, proven methods make passwords useless for hackers, even if they access your data.
Here's why hashing and salting matter, how they operate together, and how to use them appropriately with modern best practices. Keep those passwords secure.
Why Plaintext Passwords Are a Disaster
Keeping passwords exactly as users enter them is a significant security risk, but many developers still get it wrong. It is like glueing your ATM card with a sticky note with your bank PIN.
Breaches come eventually, so hackers do not even try. They read raw passwords and accessed your users' accounts. The worst part is that most people reuse passwords, which opens up other sites.
The good news? If properly hashed and salted, a stolen password hash is less helpful to an attacker.
What Is Hashing?
Please note: hashing is not encryption. Never “decrypt†a hash. Hashes are one-way functions that convert inputs like passwords into fixed-length strings of characters, termed fingerprints.
For instance, "MySecurePassword!" may become: $2b$12$abc1234xyz.
The original input is nearly impossible to guess with good hash algorithms. Brute-forcing a single password takes time and computer power because contemporary algorithms like bcrypt, Argon2, and PBKDF2 are purposefully slow to execute.
These proven algorithms remain the best in 2025. The old MD5 and SHA-1? Do not bother; they are fast, outdated and broken.
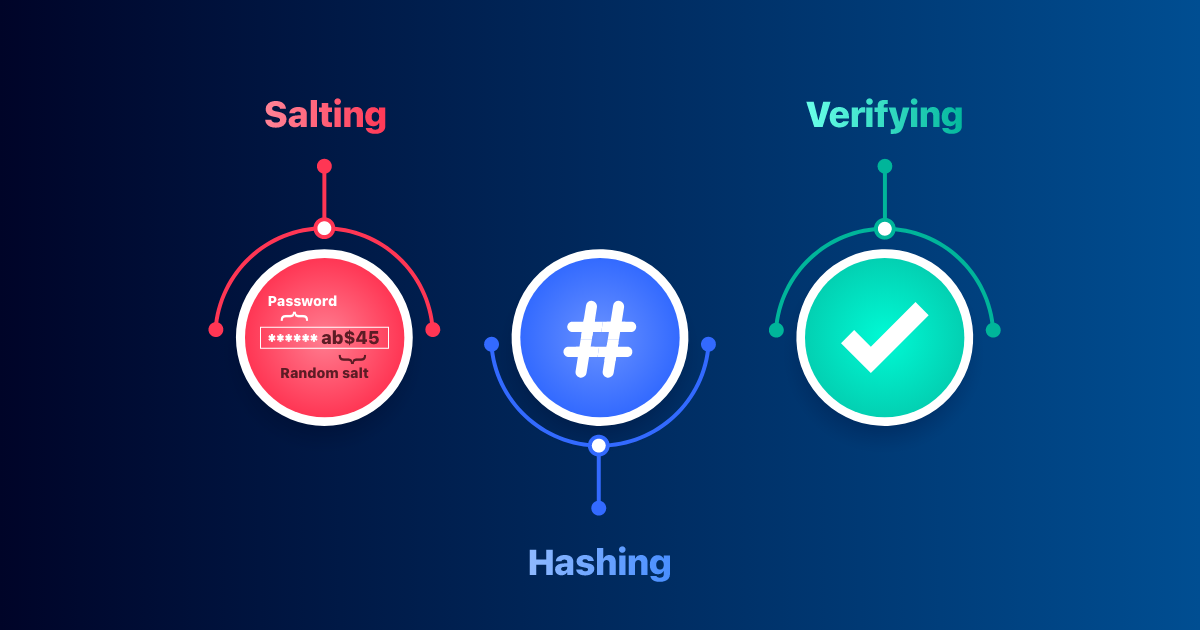
Why Salting Matters
Why salt when hashing is so good?
Problem: two users may share a password. If you hash 'Password123' for both, attackers will see identical hashes, a red signal. Worse, hackers can breach millions of accounts in seconds using 'rainbow tables'; large precomputed databases of popular passwords and hashes.
Salt resolves this. Imagine adding a secret component to each password. The string is random and added before hashing. Thus, 'Password123' + salt123 is one hash and ‘Password123’ + salt456 is another.
Hashes are unique even if two people use the same password. Rainbow tables are worthless because attackers must crack each hash individually. Much harder!
Most recent frameworks handle salts, but you have to understand their importance.
How to Hash and Salt Passwords in 2025
Okay, enough with the concept. Let's see how it works. This Node.js example uses bcrypt, but it works in Python, Ruby, PHP, and more.
Install bcrypt:
npm install bcrypt
Generate a salt & hash:
const bcrypt = require('bcrypt');
async function hashPassword(password) {
const saltRounds = 12; // More rounds = slower hashes = more secure
const hash = await bcrypt.hash(password, saltRounds);
return hash;
}
const myHash = await hashPassword('MySecurePassword!');
console.log(myHash);
Store it:
Bcrypt includes the salt in the hash output, thus you do not need to keep it separately. Useful, right?
Verifying Passwords
The hash is not ‘decrypted’ when the user logs in. Hash the password they entered with the same salt and compare.
async function verifyPassword(inputPassword, storedHash) {
const match = await bcrypt.compare(inputPassword, storedHash);
return match; // true or false
}
const isValid = await verifyPassword('MySecurePassword!', myHash);
console.log(isValid); // ✅ true if it matchesWhy is hashing so useful? It only needs one check, no decrypting, and no trouble.
Extra Best Practices for 2025
You are hashing and salting well, but you can do more to protect users:
- Use HTTPS always: Never transfer passwords or hashes across unsecure connections.
- Need strong passwords: Long passwords are tougher to hack.
- Check against known breaches: Use Have I Been Pwned's API to check for compromised passwords.
- Add multi-factor authentication: Despite guessing a password, a second factor can stop them.
- Stay updated: Use modern libraries. Do not use outdated security algorithms.
Conclusion
In 2025, password security basics include strong hashing, unique salts, and new best practices that make it hard for hackers to fetch data without use's consent. No system is fully hackproof. However, hashing and salting provide you and your users a big edge in a breach.
Get this properly today, and you will never worry about a leaked password table tomorrow.
928 views
