October 30, 2025
Mastering Edge Computing: A Developer's Guide to Reducing Latency and Optimizing Data Flow
Mastering Edge Computing: A Developer's Guide to Reducing Latency and Optimizing Data Flow
Have you ever thought about why some apps can handle data quickly and others take a long time? Edge computing is the key to data processing revolution. Imagine processing data locally without sending it to the cloud. It's interesting, right? All developers must understand edge computing for IoT, autonomous cars, and real-time analytics. Edge computing improves application speed and intelligence by reducing latency and data flow.
What is Edge Computing?
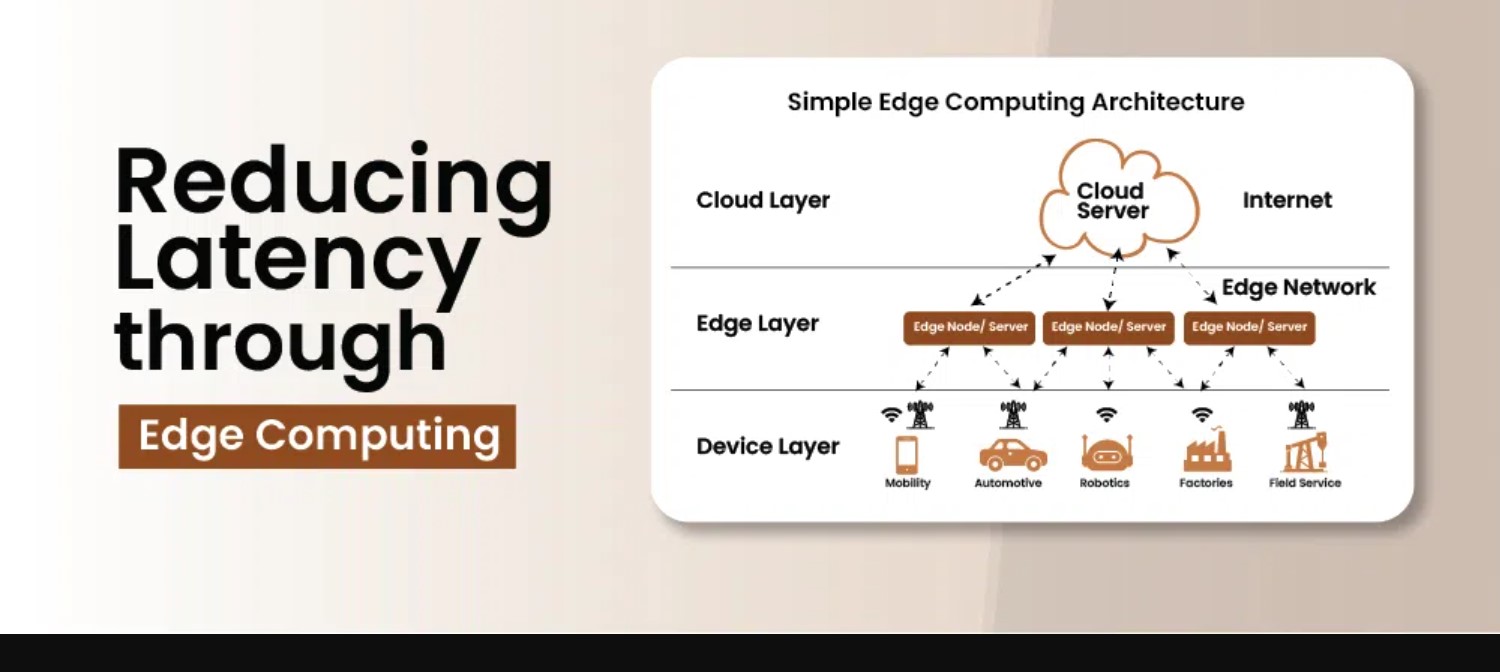
Exactly what is edge computing? Consider it smarter data processing. Traditional data processing on a central server or cloud may take time for real-time demands. Contrary to popular belief, edge computing stores data on sensors, devices, or local servers.
Avoiding extended data transmissions decreases latency and bandwidth. It also speeds up decision-making, which is vital in healthcare, industry, and smart cities where seconds matter. Developers might ask, How can I use this? No worries, we'll get to that.
Edge Computing Use Cases for Developers
Edge computing is genuine and used in real life. Talk about some fascinating use cases where it's making a big difference.
Imagine designing a smart home. Smart thermostats and webcams use edge computing to process data instantly and respond faster. It boosts system speed and efficiency.
Edge computing helps self-driving cars act quickly by analysing sensor data and avoiding barriers.
These use cases offer developers wonderful opportunity to develop responsive, efficient, and scalable apps. Edge computing helps you smarten apps for vast IoT networks or real-time healthcare data. How can you build such solutions? We'll discuss that.
How Edge Computing Reduces Latency?
The main value of edge computing is latency reduction. Sending data to a remote server for processing delays it. Real-time apps can be ruined by millisecond delays.
Edge computing processes data near its source, enabling real-time choices. No round trip to the cloud needed. Here's an example to visualise:
import time
import random
# Simulate edge computing data processing
def edge_compute(data):
return sum(data) / len(data)
# Simulate real-time data collection
def collect_data():
return [random.randint(1, 100) for _ in range(100)]
start = time.time()
data = collect_data()
result = edge_compute(data)
end = time.time()
print(f"Processed data at edge in {end - start:.4f} seconds")By computing at the edge, the code above processes data in a fraction of the time it would take over the network. That means speedier apps and happy users!
Optimizing Data Flow in Edge Computing
Now that we know edge computing minimises latency, let's optimise data flow. Data is filtered and compressed before being sent to the cloud in edge computing. Sharing only essential data minimises bandwidth and boosts efficiency.
Developers can send data to the edge and wait for a response without blocking other operations with asynchronous processing. Example of asynchronous data transmission:
import asyncio
# Asynchronous data transmission to edge server
async def send_data_to_edge(data):
await asyncio.sleep(1) # Simulate network delay
print("Data sent to edge:", data)
async def main():
data = [random.randint(1, 100) for _ in range(50)]
await send_data_to_edge(data)
asyncio.run(main())Asynchronous programming lets you send data to the edge without slowing your application. Even in heavy traffic, this keeps everything going smoothly.
Challenges and How Developers Can Overcome Them
Edge computing is great yet difficult. Development challenges include network reliability, what if the edge device loses connection? Developers must include fail-safes. You prevent app crashes by saving temporary data locally and synchronising it when the network returns. Writing resilient programming that adapts to interruptions is key. Prepare and handle errors to keep things running well in tough situations.
Conclusion
Developers must embrace edge computing, the future of coding. Building faster, more efficient real-time applications requires lowering latency and optimising data flow. Try edge computing today to make your apps smarter and more responsive!
628 views
